Configuration in a .NET Core Console Application
For .NET is a range of packages which makes it easy to work with configuration files.
All examples is made for a .NET Core Console Application, and covers a connection string.
A walkthrough is available on Youtube: .NET Core config file and the code is for the walkthrough is available on GitHub : dot-net-core-configuration-demo
A simple connection string config
In the console application add a json file to the project, you can call it appsettings.json. Set the properties of the file so that it’s copied to output directory.
This makes it possible to add the config file to your git repo.
Add the following content to the file:
{
"ConnectionStrings": {
"DefaultConnection": "Server=(localdb)\\mssqllocaldb;Database=MyApplicationDatabase;Trusted_Connection=True;MultipleActiveResultSets=true"
}
}
Add the following nuget packages (Install-Package) to the program:
- Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration
- Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration.FileExtensions
- Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration.Json
Add the following code in the Main:
var builder = new ConfigurationBuilder().SetBasePath(Directory.GetCurrentDirectory()).AddJsonFile("appsettings.json");
var config = builder.Build();
The will load the file appsettings.json into the config object.
You can now access the settings in settings file, like this:
var defaultConnectionString = config.GetConnectionString("DefaultConnection");
This can be used when initializing your Enitity Framework in your Context class.
optionsBuilder.UseSqlServer(defaultConnectionString);
Environment specific config files
Often you have settings which is environment specific, like a local database server or a local file path.
These files would not not add to your git repo, as they are often very specific, you can avoid that by adding them to the ignore-file.
I visual studio on the project can you add environment variables, like this:
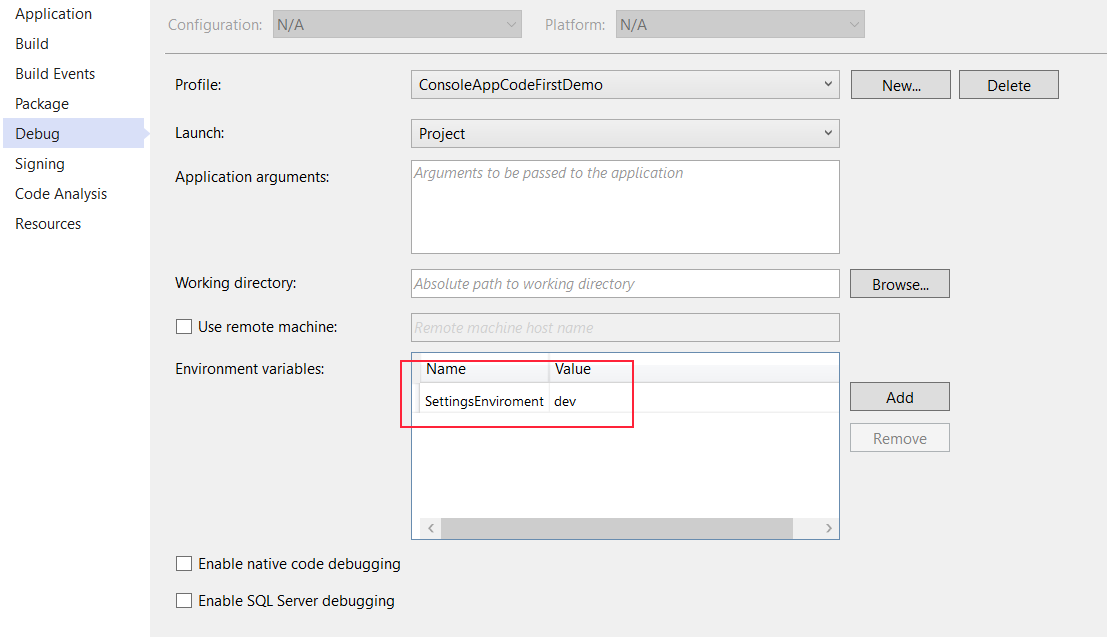
These can be accessed from the code:
var environmentName = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("SettingsEnviroment");
And be used to fetch a optional configuration file like this:
var builder = new ConfigurationBuilder().SetBasePath(Directory.GetCurrentDirectory()).AddJsonFile("appsettings.json").AddJsonFile($"appsettings.{environmentName}.json", optional: true);
What happens now is that the values in appsettings.json is overwritten by the values in appsettings.dev.json.
You can now add a json-file called appsettings.dev.json, remember to set the properties of the file so that it’s copied to output directory.
The content could be like:
{
"ConnectionStrings": {
"DefaultConnection": "Server=(localdb)\\mssql;Database=MyApplication;Trusted_Connection=True;MultipleActiveResultSets=true"
}
}
And the value defaultConnectionString now be what is defined in the dev.json file. And the idea is that this file can be different on each developers computer.